A general ledger is structured with accounts for assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses, each recording individual transactions. Having an easy-to-read general overview of your company’s finances and creating trial balances can help you spot unusual activity, or fraud quickly, so you can take action before a serious problem develops. You can also use the information on a GL to verify the accuracy of financial statements during internal reviews and audits.
What’s the difference between a journal entry and a general ledger?
The general journal is a great place to find out when accounting transactions happen. Your bookkeeper needs to set up your accounting books using the most suitable sub-ledgers for you. As a result, you and your accounting team will typically consult the general ledger whenever necessary to investigate the details of your business’ activities, transactions, and account balances. Double-entry bookkeeping records each transaction as both a debit and a credit in the general ledger, ensuring balanced accounts. Some disadvantages of a general ledger include the cost and amount of time it takes to set up.
Inventory Management Strategies to Avoid Stockouts in Business
In other words, a ledger is a record that details all business accounts and account activity during a period. You can think of an account as a notebook filled with business transactions from a specific account, so the cash notebook would have records of all the business transactions involving cash. “General ledgers are maintained to make a balance sheet, file taxes and most importantly, view all your information in one place,” said Salman Rundhawa, founder and CEO of FilingTaxes.
Step #2: Post journal entries
Unlike pperating expenses, the non-operating incomes and expenses are one-time incomes or expenses that you either earn or incur. Neither are an outcome of your core business activity, nor are such expenses related to your core business operations. Operating what is a qualified retirement plan income includes sales revenue, income received as fees and commission, etc., and these incomes will depend on the type of business you undertake. In this instance, a subsidiary ledger records detailed information of the related control account.
Businesses have an expansive list of accounts, so you will need to make as many as required to track all transactions. Revenue accounts in the general ledger are typically divided into categories, such as sales and interest. For example, sales may be further divided into retail sales and wholesale sales, or foreign sales and domestic sales. Although there are many possible accounts in a general ledger, they can all usually be classified into permanent and temporary categories. Let’s look at some of the accounts small businesses may use in the general ledger.
A Balance Sheet Transaction Example
Due to all of these features, the ledger is sometimes called the king of all the books of accounts. The ledger is the principal book of accounts in which transactions of a similar nature relating to a particular person or thing are recorded in classified form. Each journal entry should have an account number, a date, a dollar amount, and a brief entry description. These detailed entries tell you the who, the what, the when, the where, and the why—leaving no room for confusion, thus creating clearer transaction explanations.
- Here is an example of how you can transfer the journal entries to a general ledger.
- This is to ensure that each transaction affects the balance sheet in such a way that an increase on one side of the balance is offset either by a decrease on the same side or by an increase on the other side.
- For example, when furniture is bought on credit for $4,000 from Fine Furniture Co., we will need to make an entry of $4,000 on the debit side of the furniture account (i.e., because this asset is increasing).
- Also known as the general ledger, the ledger is a book in which all accounts relating to a business enterprise are kept.
- Sub-ledgers within each account provide details behind the entries documented in account ledgers, such as if they are debited or credited by cash, accounts payable, accounts receivable, etc.
- Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching.
Liabilities are the amounts owed to individuals or outsiders, and are the financial obligations you’re bound to fulfill. These are the obligations that you have to fulfill the amounts you have borrowed and which have not yet been paid for. Assets are the resources your business owns, and these resources have the capacity to generate cash flows. Assets are items of economic value that can be converted into cash or cash equivalents. Expenses consist of money paid by the business in exchange for a product or service.
All of the accounts in the chart of accounts are summarized and categories in the general ledger. As a business owner, you can use small business software and bookkeeping professionals to minimize your accounting responsibilities. However, you must still be able to comprehend your company’s financial data to properly make strategic business decisions.
As a company must account for all their financial transactions, the GL accounts act as a record of all transactions involving that specific account. These entries correspond with the company’s journal entries, which track all increases and decreases to accounts. General ledger accounting is the process of recording and categorizing all of a business’s financial transactions in one centralized ledger.
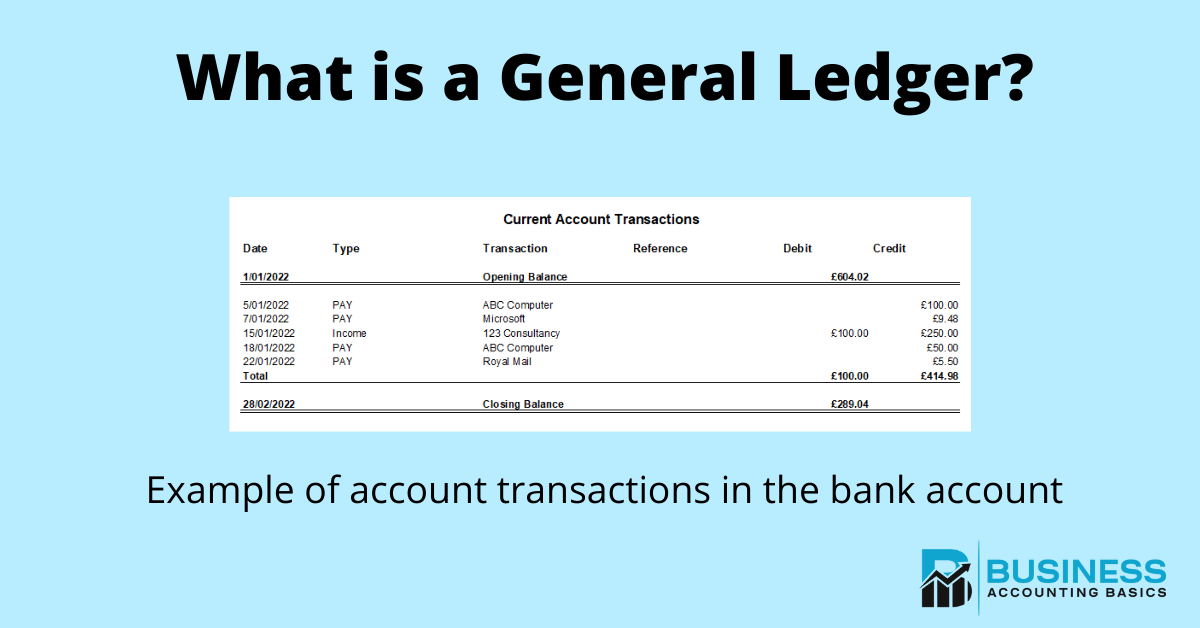
Instead, financially-minded individuals — and businesses — use ledgers to fastidiously document money that’s they’re paying out, or being paid. On January 31, after all of the cash journal entries post, the general ledger lists the ending cash balance. Now let’s move on to talk about debits vs. credits and how they work in an accounting system. Accounting ledgers can be displayed in many different ways, but the concept is still the same. One way to avoid errors is to use a POS system like Lightspeed Retail, which connects with accounting software to automatically sync data. To learn more about what Lightspeed Retail can do for your business, talk to an expert today.


